AMF Security OpenFlow Authentication Flow
This section describes the flow of terminal authentication in an OpenFlow configuration.
AMF Security performs authentication at the request of the OpenFlow Switches it manages.
OpenFlow Switches ask AMF Security for authentication in the following manner.
- OpenFlow Switch receives packets from the terminal
- The OpenFlow Switch checks whether a flow entry has been registered for the source MAC Address of the terminal's packet. When a matching flow entry is found, the OpenFlow Switch transmits the packet according to the flow entry.
- If there is no matching flow entry, the OpenFlow Switch sends a packet to query AMF Security.
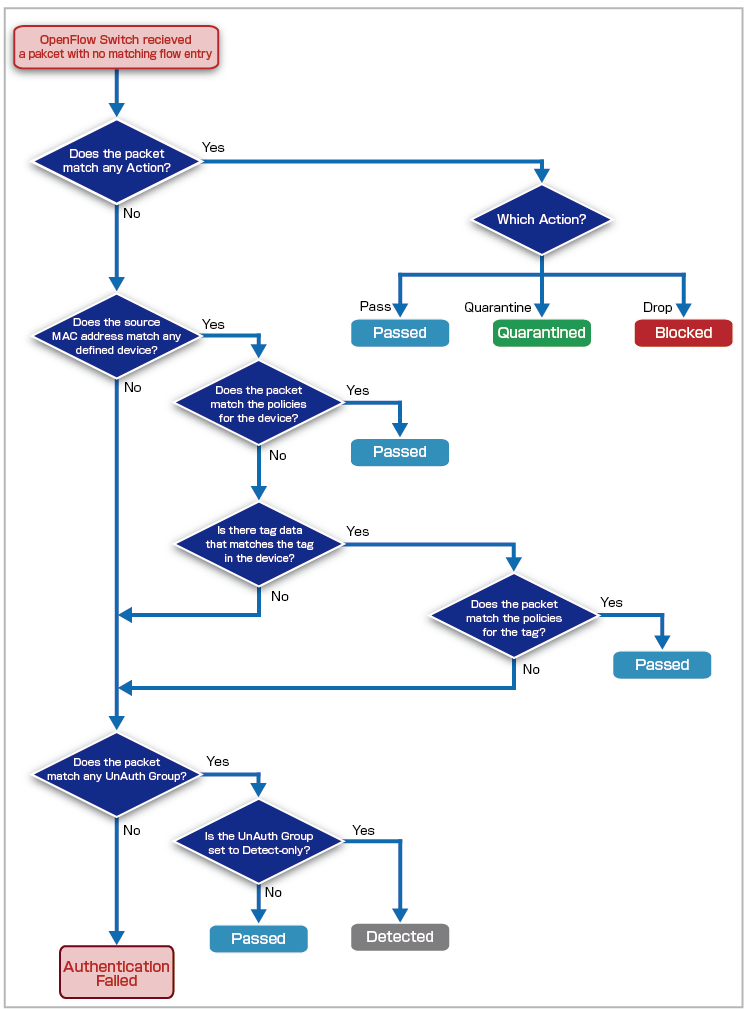
AMF Security has four major authentication processes: Device Authentication Data, Authentication using Tag, UnAuth Group and Action.
- Device Authentication Data
The network (VLAN) to connect to is determined based on the security policy (Policy) of the Device ID (Device) associated with the MAC Address.
- Authentication using Tag
The VLAN to connect to is determined based on the policy set on the tag, not the policy of the device with which the MAC Address is associated.
- UnAuth Group
For MAC Addresses that are not registered in Device Authentication Data, the connection destination VLAN is determined based on the policy set for the UnAuth Group.
- Action
Individually discard/isolate or specify the destination VLAN for terminals that match the conditions of the device's MAC Address, IPv4 Address, Device, Device Tag, Location, OpenFlow Switch, and Connecting Network, or specify the destination VLAN. It is possible to manually create actions similar to the ones provided by interacting applications.
As an example, the behavior in the case where Action, Device Authentication Data, and UnAuth Group are registered is shown.
| Action ID: Drop | |
| Condition | MAC Address 00:00:00:00:00:01 |
| OpenFlow/TQ Action | Drop(Block) |
| Device ID: Device_A | |
| MAC Address | 00:00:00:00:00:01 |
| Policies | VLAN100 |
| Device ID: Device_B | |
| MAC Address | 00:00:00:00:00:02 |
| Policies | VLAN101 |
| Group ID: Unregistered | |
| Policies | VLAN200 |

- The MAC Address "00:00:00:00:00:01" is registered in both "Action ID: Drop" and Device Authentication Data of "Device ID: Device_A". If the device authentication processing meets the conditions of the action that is performed first and Drop(Block) is applied, subsequent authentication processing of Device Authentication Data is not performed.
- The MAC Address "00:00:00:00:00:02" matches Device Authentication Data of "Device ID: Device_B", so it is connected to VLAN101.
- If the MAC Address "00:00:00:00:00:03" is not registered in AMF Security, it is connected to VLAN200 of UnAuth Group because it does not match the registered Device Authentication Data. Note that since no location or schedule is set in UnAuth Group policy, all devices (MAC Addresses) that are not registered with AMF Security is connected to VLAN200.
02 Aug 2024 15:10