MAC Address Authentication
MAC Address Authentication is a mechanism to authenticate a wireless client by its MAC address when the client wants to associate to an AP.
There are two methods for MAC Address Authentication to check the validity of clients' MAC addresses. One is using RADIUS servers, and the other is using MAC Address Lists configured with the AWC Plug-in.
When you use the AWC Plug-in's MAC Address List, you can assign a single MAC Address List to each AP Profile. If an AP Profile has more than one VAP configured, you can choose whether to use the single MAC Address List on all VAPs, or to use the MAC Address List on some VAPs and use separate RADIUS servers on other VAPs.
NoteMAC Address Authentication is only supported by TQ series.
NoteMAC Address Authentication is valid for TQ2450, TQ3200, TQ3400, TQ3600, TQ4400, TQ4600, TQ4400e, TQ1402, TQ5403, TQ5403e, TQm1402, and TQm5403 running normal firmware, and for TQ5403 and TQ5403e running SDN/OpenFlow compatible firmware. TQ4400 and TQ4600 running SDN/OpenFlow-capable firmware are not supported.
NoteWhile MAC Address Authentication checks the validity of a client, it does not improve the security level of the wireless communication itself. It is recommended that WPA Personal or WPA Enterprise is used for authentication and encryption in addition to the client validation by MAC Address Authentication.
If you use WPA Enterprise along with MAC Address Authentication, RADIUS attributes used for determining client VLANs should be configured as the ones for WPA Enterprise, not for MAC Address Authentication.
To use MAC Address Authentication, enable "MAC Address Authentication" on a VAP. Please refer to Configure AP Profiles for more details.
Use MAC Address List on AWC Plug-in
- First, you have to create a MAC Address List. Refer to Configure MAC Address Lists for more details.
You have to choose an action, either "Allow" or "Deny" for a new MAC Address List to create.
- "Allow" creates a whitelist, which only permits traffic from the MAC addresses in the list and blocks all other traffic.
- "Deny" creates a blacklist, which only blocks traffic from the MAC addresses in the list and permits all other traffic.
- "Allow" creates a whitelist, which only permits traffic from the MAC addresses in the list and blocks all other traffic.
- To use an external RADIUS server for MAC Address Authentication, you have to create an AP Profile. Refer to Configure AP Profiles for details.
The following two items are related to MAC Address Authentication:
- Specify a MAC Address List to use in the "System" section's "MAC Address List".
Clicking the "MAC Address List" drop-down list shows the "Select MAC Address List" dialog box. Click a MAC Address List for use with VAPs defined in the AP Profile and click "Select".
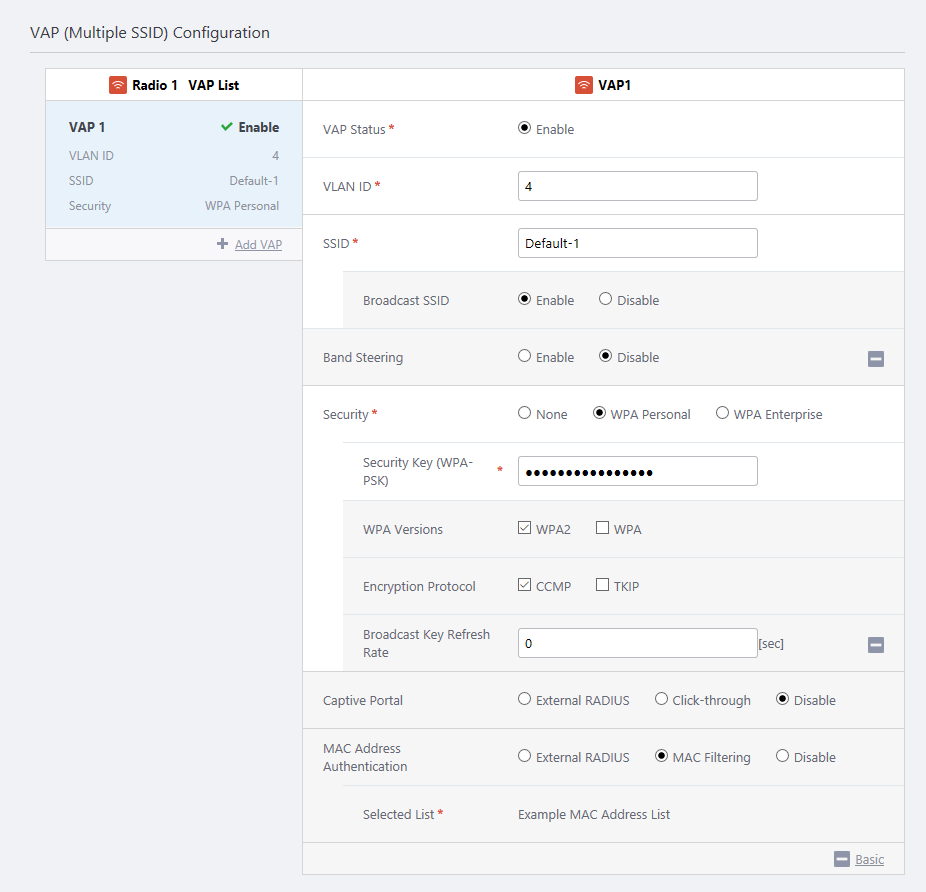
- In the "VAP (Multiple SSID) Configuration" section, select "MAC Filtering" for each VAP on which you want to use MAC Address Authentication using the list.
When you select "MAC Filtering", the MAC Address List selected in the "System" section will be shown in the "Selected List" field.
Note
You cannot use separate MAC Address Lists for VAPs configured on a single AP Profile. If you want to use a different set of MAC Addresses for each VAP, you have to use external RADIUS servers.
- Specify a MAC Address List to use in the "System" section's "MAC Address List".
Use External RADIUS Server
To use an external RADIUS server for MAC Address Authentication, you have to create an AP Profile. Refer to Configure AP Profiles for details.In the "VAP (Multiple SSID) Configuration" section, select "External RADIUS" for each VAP on which you want to use MAC Address Authentication using RADIUS servers.
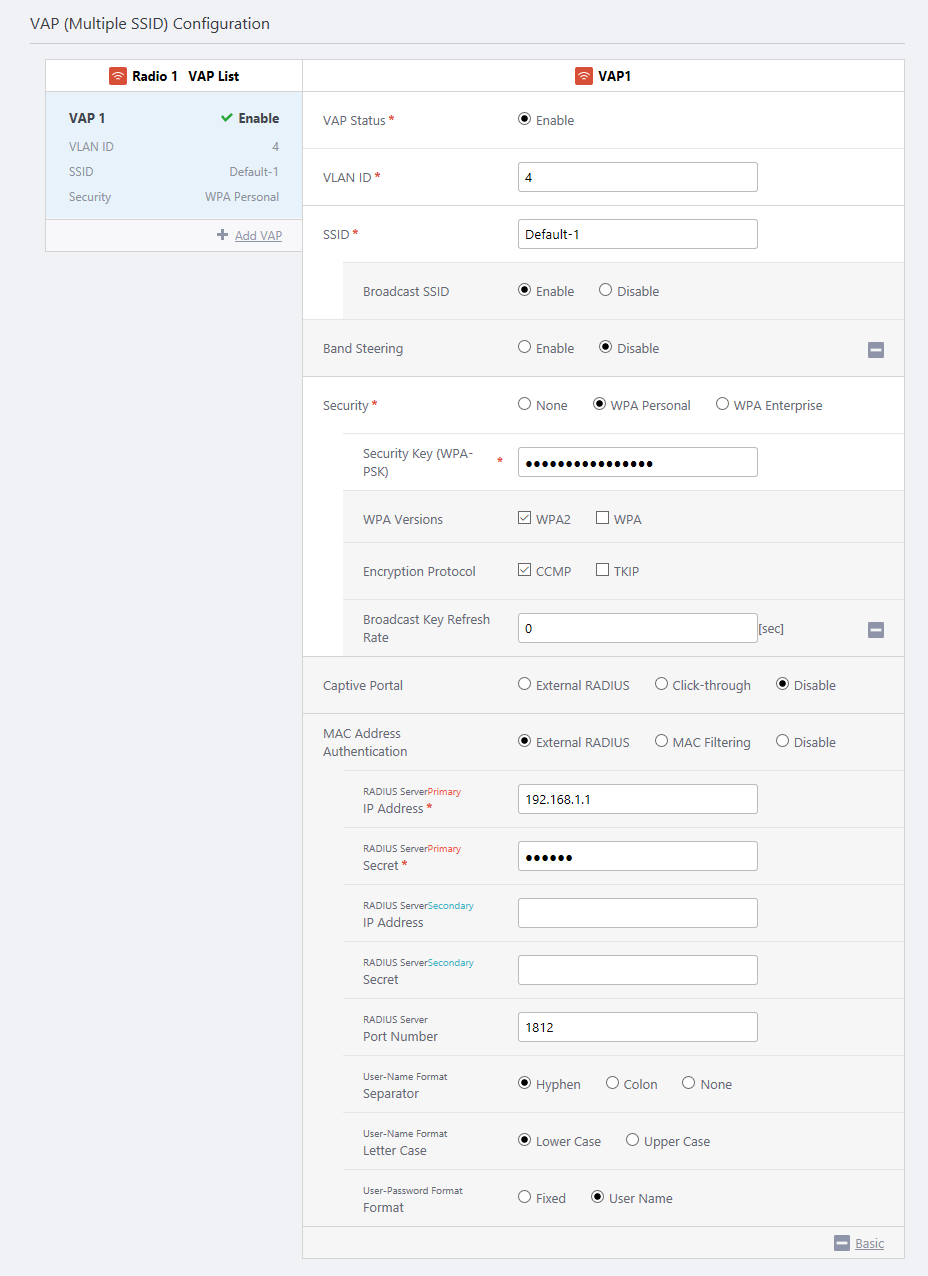
When performing MAC Address Authentication, the AWC Plug-in sends a client's MAC address to the RADIUS server as a username. Therefore, you have to use the same MAC address format on both the AWC Plug-in and the RADIUS server.
NoteRefer to the RADIUS server's documentation for detailed instructions of how to configure the server.
| Item Name | Description |
|---|---|
| User-Name Format Separator | Specify an octet delimiter to use in a User-Name attribute from "Hyphen", "Colon" and "None". The default is "Hyphen". |
| User-Name Format Letter Case | Specify which case to use in a User-Name attribute from "Upper" and "Lower". The default is "Lower". |
| User-Password Format | Specify what is used for a User-Password attribute when a client MAC address is sent to the RADIUS server for authentication. The default is "User Name". If you select "Fixed Password", a string specified in "User-Password Format Password" is always used as the value of User-Password attribute. If you select "User Name", the same string as the User-Name attribute (MAC Address) is sent to the RADIUS server as the value of User-Password attribute. |
| User-Password Format Password | Specify a fixed password string which is used when "User-Password Format Type" is set to "Fixed Password". |
By default (where "User-Name Format Delimiter" is "Hyphen", "User-Name Format Case" is "Lower" and "User-Password Format Type" is "User Name"), authentication credentials (User-Name and User-Password attributes) of a client will be sent to the RADIUS server as follows:
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| User-Name | Full Name | MAC Address. Lower Case, Delimited by hyphen (eg. ab-cd-ef-12-34-56) |
| User-Password | Password | Same as the User-Name. (eg. ab-cd-ef-12-34-56) |
Configure RADIUS Server
To use Dynamic VLAN, you have to add the APs to the RADIUS server's database as RADIUS clients.| Item Name | Description |
|---|---|
| RADIUS Client's IP Address | Wireless AP's IP Address (Example) 192.168.1.230 |
| Secret | Wireless AP's Password (Example) "MyPassword" |
NoteBecause client users are authenticated by APs, you have to add all APs to the RADIUS client database.
Dynamic VLAN
MAC Address Authentication supports Dynamic VLAN directly, and can assign each client (user) to a particular VLAN that is specified as RADIUS attributes during MAC Address Authentication.When used with WPA Enterprise
When you use WPA Enterprise along with MAC Address Authentication, a wireless client is assigned to the VLAN that was determined during WPA Enterprise authentication.In other words, if an AP receives VLAN attributes during a WPA Enterprise authentication for the client, the AP assigns the VLAN to the client.
If the AP doesn't receive any VLAN information during a WPA Enterprise authentication, the client's traffic will be handled on a VLAN that is configured for the VAP.
As a result, VLAN attributes that are received during MAC Address Authentication will be discarded.
NoteWhen Captive Portal, MAC Address Authentication, and WPA Enterprise are used together, they are processed in the order of "MAC Authentication" -> "WPA Enterprise" -> "Captive Portal".
28 May 2020 09:34