About AT-RADgate
Positioning of AT-RADgate
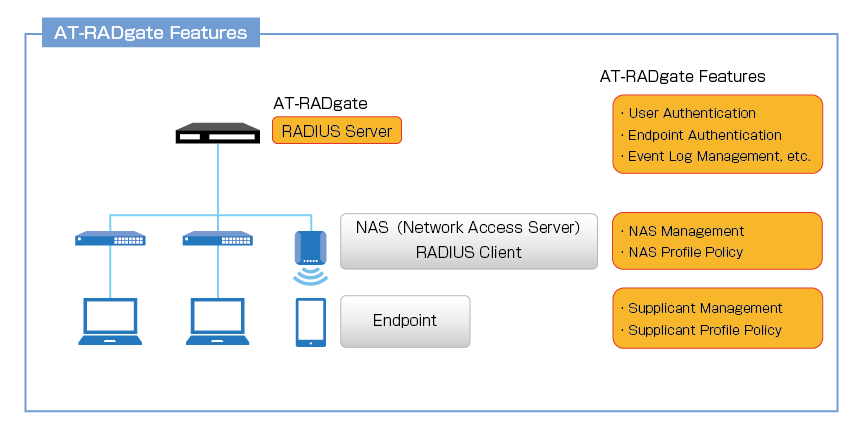
AT-RADgate is a RADIUS Authentication Server.This is a general RADIUS Server function that complies with IETF standards. In addition, by using it in combination with Allied Telesis network products, it is possible to perform advanced control of clients connected to the managed network.
Glossary
AT-RADgate uses the following terms:| Glossary | Description |
|---|---|
| RADIUS Server | A server that provides Authentication services using the RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) protocol. This is the basic function of AT-RADgate. |
| NAS (Network Access Server) RADIUS Client |
This is a device that has an interface to connect to Endpoints and sends Authentication requests to a RADIUS Server. At AT-RADgate it is called NAS. In a network configured with Allied Telesis products, Edge Switches and Wireless LAN Access Points that support AW+ can be used as NAS. |
| Endpoint | This is the device that connects to the NAS. Also called Supplicant. |
| Authentication | This refers to the RADIUS Server process that verifies the legitimacy of the User or Endpoint being authenticated in response to an authentication request from the NAS. |
| Authorization | This refers to the RADIUS Server process that determines the privileges to be assigned to the User or Endpoint that has been successfully authenticated. |
| Authentication policy | These are the rules that AT-RADgate uses to determine whether a request is legitimate and should be approved. Authentication policies are classified into five categories: User policy, Endpoint policy, NAS policy, NAS Profile policy, and Supplicant Profile policy, and can be used for Authentication and Authorization. |
Authentication Method
AT-RADgate supports the following authentication methods.- PAP
- EAP-MD5
- EAP-PEAP
- EAP-TLS
- EAP-TTLS(PAP, MS-CHAPv2)
NoteAll authentication protocols are enabled at all times. Cannot be disabled.
User Authentication and Endpoint Authentication
Standard RADIUS Authentication involves authenticating the user identified by the User-Name attribute in the authentication request message. In addition, AT-RADgate provides a user endpoint authentication function using the MAC Address stored in the Calling-Station-Id attribute of the authentication request message.Authentication, Authorization and Authentication policy
AT-RADgate processes authentication requests from registered NAS (Network Access Server) based on registered user or endpoint information. The RADIUS protocol is used to communicate with the NAS. This process consists of two phases:| Process | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Authentication | Verify the authenticity of the authenticated User or Endpoint |
| Authorization | Determines the permissions assigned to the authenticated User or Endpoint |
| Policy Name | Description |
|---|---|
| User | Define users for access control. The attribute value set for the user whose user name and password match during User Authentication is assigned. Authentication fails for users who do not match any policy. |
| Endpoint | Defines the endpoints for which access is controlled. This is referenced during endpoint authentication, and the attribute value set is assigned to endpoints with a matching MAC Address. Endpoints that do not match any policy are assigned the attribute of unregistered endpoint. |
| NAS | Defines the device that provides access control for a user or endpoint. |
| NAS Profile | Define the configuration parameters for NAS. |
| Supplicant Profile | Define the parameters to be assigned to authorized supplicants. |
NAS policy
AT-RADgate authenticates the sender of the received RADIUS message and processes only those that pass. Authentication is determined by whether the source IP Address of the message and the pre-shared key stored in the message match those registered in NAS policy.The endpoint authentication function is also enabled through NAS policy. When you assign a NAS Profile with endpoint authentication settings to a NAS device that has endpoint authentication enabled, endpoint authentication is performed in addition to user authentication for authentication requests sent by that NAS device.
User Authentication and Endpoint Authentication policy
AT-RADgate provides user authentication and endpoint authentication functions. The authentication function detects the destination NAS of the supplicant that sent the access request, the user making the connection, and the endpoint being operated by the user. If the NAS and user information match those registered in the authentication policy, the connection is allowed; otherwise, the connection is denied.User authentication is an IETF standard authentication method, and all authentication request messages are compared against AT-RADgate's User policy, except for the special cases listed below.
- When an EAP-PEAP authentication request is received while linked to Windows Active Directory, user authentication is performed using the Windows Active Directory database rather than the device's own authentication policy.
- If endpoint authentication is enabled and MAC-based Authentication request is received, only device authentication is performed, not user authentication.
NoteTerminal authentication is performed by comparing the MAC Address with the AT-RADgate Endpoint policy when the MAC Address is stored in the Calling-Station-Id attribute of the authentication request message sent by a NAS with valid endpoint authentication settings. If authentication is successful, the device is assigned the attributes of an authenticated device. If authentication fails, the device is assigned the attributes of an unregistered device.MAC-based Authentication request is a request in which the received authentication request message meets the following requirements:
- PAP or EAP-MD5 message
- The User-Name value is a string that represents the MAC Address
Authorization
AT-RADgate can assign additional settings to users or devices that have been successfully authenticated. Additional settings are registered in the authentication policy as a Supplicant Profile. Supplicant Profiles are assigned priorities, and authenticated users or endpoints are matched with Supplicant Profiles in order of priority, and the settings information of the first matching profile is assigned to the user or endpoint.Supplicant parameter
The supplicant that made the access request is assigned the destination NAS, user, and endpoint information through the authentication process. The combination of this information is the Supplicant parameters, and these Supplicant parameters are compared during the Supplicant Profile matching process in the authorization process. The Supplicant parameters are:- Endpoint MAC Address
- Endpoint Name
- Registered devices/Unregistered devices
- Access Level
- Tag
Note◼ Access LevelThe contents of the Supplicant parameters cannot be viewed because they are used internally by AT-RADgate.
A number between 0 and 15 that can be set in User and Endpoint policies, indicating the strength of the access authority of the target indicated by the policy. A value of 0 means that access is not allowed, while values 1-15 are allowed, with higher numbers indicating greater privileges. The smaller of the access levels set in the User policy assigned to the supplicant and the Endpoint policy is adopted.
◼ Tag
A string that can be set for NAS policies, User policies, and Endpoint policies. Multiple tags can be set for each policy. Represents the group to which the policy's subject belongs. The tag of the Supplicant parameter is the sum of all the tags of each policy assigned to the supplicant.
Supplicant Profile
Supplicant Profile mainly consists of priority, Supplicant parameter match conditions, and Supplicant settings.The priority is a number between 1 and 15, and Supplicant parameters are matched in order from the profile with the lowest priority value.
NoteThe Supplicant parameter matching criteria specifies the conditions for the supplicants to which this profile applies. The conditions that can be set are as follows:If the priorities of Supplicant Profiles are the same, the order in which the Supplicant Profiles are matched is undefined. Therefore, if you want to explicitly separate the conditions, be sure to set the priority to a different value.
- All endpoints
- Endpoint MAC Address
- Registered devices
- Unregistered devices
- Endpoint Name
- Access Level
- Tag
- Action
- VLAN
- Filter ID
- Filter Rule
02 Oct 2025 12:05