What is AT-SESC
Where does AT-SESC Fit In
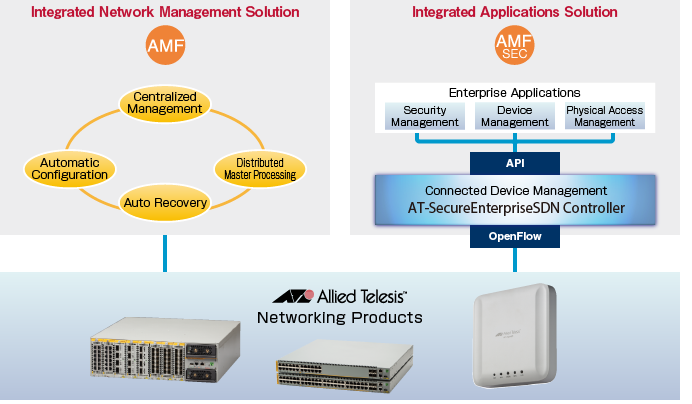
AMF-SECurity (AMF-SEC) is our solution to streamline network operations and enhance security in office environments.In its scenario, AT-SESC functions as an SDN controller in the core of connected device management system.
It makes a whole system administration more efficient along with AMF (Allied Telesis Management Framework), which is our solution to centralize and simplify network device management.
What does AT-SESC Manage (OpenFlow)
AT-SESC can centrally control the network access from various devices by installing packet control flows for the devices' MAC address on the OpenFlow Switches it manages.AT-SESC controls network traffic by using the OpenFlow protocol over the TCP connections established with the switches.
For each device, administrators can define two conditions on AT-SESC, where and when the device can access the network. The first one is called "Location" and the other is called "Schedule".
Condition can be more granular like "From this OpenFlow Switch in that location" or "on this particular switchport of the switch in that location".
If a device meets those conditions, it is allowed to join the logical network defined by a VLAN ID.
Those elements are collectively referred to as security policies. Here is a list of elements of security policies:
- Location
Where a device can access the network.
By associating OpenFlow Switches with a location, you can define a physical network space.
- Schedule
When a device can access the network.
You can specify a period of time with a Start Date / Time and End Date / Time.
- OpenFlow Switch
OpenFlow Switches from which a device can access the network.
You can allow a device to access the network only when it connects to a specific OpenFlow Switch.
- Switch Port
A port on an OpenFlow Switch from which a device can access the network.
You can allow a device to access the network only when it connects to a specific port on a particular Switch.
- Network
A VLAN subnet to which a device can belong (a logical network space defined by a VLAN ID).
The MAC address interface of the device is managed by connecting, blocking, and isolating based on the security policy assigned to the device.
A device can have more than one MAC address interface.
Assuming that a device has two MAC addresses - one for a wireless interface and the other for a wired interface, both of them can access the same network if they meet the conditions for Location and Schedule.
| Device Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device | network-capable equipment which connects to an OpenFlow Switch | ||||
| └ | MAC Address | a MAC address of the device interface | |||
| (multiple items can be defined) | |||||
| └ | Security Policies | Network | a VLAN segment (VLAN ID) to which a device is assigned. | ||
| Location | a physical location where a device can access the network. | ||||
| └ | OpenFlow Switch | a switch in the location. | |||
| └ | Switch Port | a port on the switch from which a device can access the network. | |||
| (multiple items can be defined) | |||||
| Schedule | a range of time during a device can access the network (Start Date / Time, and End Date / Time). | ||||
| (multiple items can be defined) | |||||
OpenFlow Switches have two types of network ports: control plane ports and data plane ports. The former is used for communicating with OpenFlow controllers while the latter is used for delivering user traffic and controlled by OpenFlow protocol.
In AT-SESC, data plane ports are further categorized into "upstream port" and "client port".
- Upstream Port
A port connected to an uplink network. An OpenFlow Switch can have only one upstream port.
- Client Port
All ports other than the upstream port. User devices are connected to the client ports.
By default, a switch port with the lowest OpenFlow port number is configured as the upstream port. This can be changed on each OpenFlow Switch.
What is AMF Application Proxy
The AMF Application Proxy controls traffic from edge devices, which are connected to AMF Members (Edge Nodes) where AMF Master (Proxy Node) authenticates the devices by querying AT-SESC (AMF Application Proxy Whitelist).It is also possible for AT-SESC to notify the AMF Proxy Node of suspected node and make Edge Nodes to block the devices (AMF Application Proxy Blacklist).
Note◼ AMF Application Proxy Whitelist and AMF Application Proxy Blacklist
・ A Proxy Node also can be an Edge Node.
・ Cannot be linked with AMF controller.
◼ AMF Application Proxy Whitelist
・ Use Virtual Chassis Stack (VCS) to provide redundancy to the AMF Master.
・ When linking with multiple local masters under AMF controller, make each local master a separate area.
To use the AMF Application Proxy, you have to configure all of AT-SESC, Proxy Node and Edge Nodes.
What does AT-SESC Manage (AMF Application Proxy Whitelist)
AT-SESC can centrally control the network access from various devices by utilizing the port authentication feature on the AMF Members it manages.The AMF Application Proxy Whitelist is an AMF-SEC (AMF-SECurity)'s integration feature where AMF devices ask the AT-SESC's whitelist server if a specific device can be allowed access to the network.
If a device meets those conditions, it is allowed to join the logical network defined by a VLAN ID.
- Location
Where a device can access the network.
By associating AMF Members with a location, you can define a physical network space.
- Schedule
When a device can access the network.
You can specify a period of time with a Start Date / Time and End Date / Time.
- Switch Port
A port on an AMF Member from which a device can access the network.
You can allow a device to access the network only when it connects to a specific port on a particular Switch.
- Network
A VLAN subnet to which a device can belong (a logical network space defined by a VLAN ID).
The MAC address interface of the device is managed by connecting, blocking, and isolating based on the security policy assigned to the device.
A device can have more than one MAC address interface.
Assuming that a device has two MAC addresses - one for a wireless interface and the other for a wired interface, both of them can access the same network if they meet the conditions for Location and Schedule.
| Device Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device | network-capable equipment which connects to an AMF Member | ||||
| └ | MAC Address | a MAC address of the device interface | |||
| (multiple items can be defined) | |||||
| └ | Security Policies | Network | a VLAN segment (VLAN ID) to which a device is assigned. | ||
| Location | a physical location where a device can access the network. | ||||
| └ | AMF Member | a switch in the location. | |||
| └ | Switch Port | a port on the switch from which a device can access the network. | |||
| (multiple items can be defined) | |||||
| Schedule | a range of time during a device can access the network (Start Date / Time, and End Date / Time). | ||||
| (multiple items can be defined) | |||||
NoteTo use this feature, your Proxy Node and Edge Nodes must have AlliedWare Plus firmware version 5.4.9-0.x or later installed.
Blocking with AMF Application Proxy
Notifying Proxy Node of Suspected Node Information
AT-SESC notifies the Proxy Node of suspected node when receiving information from security software or devices that detect suspected terminals, or adding an action on the Policy Settings > Add Action page. The suspected node's information is stored on AT-SESC and can be viewed on the Policy Settings > Action List page.Those elements are collectively referred to as security policies. Here is a list of elements of security policies: AT-SESC does not notify the proxy node of the information again.
NoteIf the proxy node holding the suspected node information reboots, the information is removed from the proxy node.
Because the proxy node cannot receive the information from AT-SESC again, the proxy node cannot relearn the suspected node automatically.
To manually tell the proxy node about the suspected node, follow the steps:
1. Open the Policy Settings > Action List page.
Those elements are collectively referred to as security policies. Here is a list of elements of security policies: 2. Click the "Export to CSV" button to save a CSV file.
3. Open the System Settings > Maintenance page.
4. In "Authentication Data" section's "Import authentication data." field, click "Browse" to specify the exported CSV file and click "Import".
AMF Actions
When AT-SESC notifies the Proxy Node of suspected nodes, it can also specify a blocking action (AMF action).AT-SESC can specify the following AMF actions:
- Drop Packets
- Link-Down
- Quarantine
- AMF Dependency
- IP-Filter
- Log-Only
When "AMF Dependency" is selected, AT-SESC does not send the AMF action, but the AMF action set on the edge node side is executed.
NoteIf AT-SESC and AMF Master receive suspected node information from multiple sources (e.g. external applications), specify the same AMF action for all the sources.
The AMF Action for each application can be specified in the "Rules" section on the System Settings > Trap Monitor Settings page.
To change the AMF action for a suspected node which has already been registered on the Policy Settings > Action List page, delete the existing action and recreate it.
NoteThe Quarantine action cannot be used on a whitelist port. Other actions can be used on the port. Even when a node is allowed by the whitelist, its traffic may be blocked in case other action matches the node.
Unblocking Suspected Nodes
To unblock a suspected node (delete the suspected node information), delete the corresponding action on the Policy Settings > Action List page. When the action is deleted, AT-SESC tells the proxy node to delete the suspected node information.NoteYou can also unblock the suspected node by running commands on the proxy node. But in this case, the proxy node does not request AT-SESC to delete the node information. So AT-SESC keeps the suspected node information. If you want to delete it, manually delete the action on the Policy Settings > Action List page.
Refer to the AlliedWare Plus Product's command reference manual for the commands.
Displaying and Emailing Blocking Status of the Suspected Node
Status of the suspected node which has been applied an AMF action by an edge node can be view on the Device > Active Device List page.AT-SESC regularly gets this information from the proxy node at 30 second interval.
NoteTo use this feature, your Proxy Node and Edge Nodes must have AlliedWare Plus firmware version 5.4.8-1.x or later installed.
By using AT-SESC's Email Notification Settings, you can also get email notifications of blocking.
- "Send Email Notification on Block Event" : An email is sent when a node is blocked by one of "Drop Packets", "Link-Down" or "IP-Filter" actions.
- "Send Email Notification on Quarantine Event" : An email is sent when a node is quarantined by "Quarantine" action.
NoteWhen AT-SESC queries the proxy node and finds that suspected node information is changed (e.g. a node moved to other switch and got blocked there again), AT-SESC updates the information on the Device > Active Device List page and sends an email notification.
Configuring AMF Master (Proxy Node) and AMF Members (Edge Nodes)
Refer to the AlliedWare Plus Product's command reference manual for how to configure Proxy Node and Edge Nodes.Depending on the AlliedWare Plus product model you use for a Proxy Node, you may have to install the proper license on the products.
NoteTo view the blocking status of suspected nodes and use email notification, please run "atmf topology-gui enable" command on AMF Master (Proxy Node) in addition to the AMF Application Proxy's basic configurations.
Configuring AT-SESC
To use AMF Application Proxy on AT-SESC, you have to configure an IP address, level 15 (privileged) username and password of the AMF Master (Proxy Node) on AT-SESC.- Open the AMF > AMF Application Proxy Settings page.
- Click "Add".
- Enter an IP address of the AMF Master (Proxy Node) in "IPv4 Address".
- Enter a username and a password for a level 15 (privileged) user account on the AMF Master (Proxy Node).
- Click "Submit".
NoteWhen you move to other page after this configuration, the Login screen is displayed. The configuration has been successfully completed. Just login again please.
When you finish this configuration, AT-SESC starts regular queries to the AMF Master (Proxy Node) at 30 second interval.
Refer to System Settings > Trap Monitor Settings for how to configure integration options with external applications.
Supported OpenFlow Switches
List of OpenFlow Switch models supported by AT-SESC can be found on the release notes of AT-SESC, switches and wireless access points.Please find those documents on our website.
https://www.alliedtelesis.com
Application Integration Solutions
AT-SESC can be used with other applications such as threat detection, device management and HR management in order to further enhance network administration efficiency and security.The latest information on the services or applications which can be integrated into AT-SESC system is published under the AMF-SEC Technology Partner Program. Contact our sales engineer for the Technology Partner Program.
14 Jun 2021 09:30